Contract management plays a central role in commercial exchanges, but it remains a time-consuming and complex activity. Between drafting, validation and signature, companies have to manage a significant flow of documents, mobilizing resources and creating risks of error.
Automated contract management is transforming this reality. By digitizing and systematizing the steps in the contract cycle, organizations are streamlining their processes, securing their data and accelerating their turnaround times. This article details why and how automating contract management can transform the way sales, legal and administrative teams work.
Sommaire
What is contract management automation?
Automation is the use of technological solutions to reduce manual tasks in contract management. In concrete terms, this means centralizing drafting, validation, signature and follow-up in a digital environment.
Rather than handling Word or PDF files sent by e-mail, each stage is structured in a tool: standardized templates, automated approvals, electronic signature and secure archiving. The entire life cycle of a contract is thus managed in a single interface.
Why automate contract management?
In a commercial environment where speed and reliability have become decisive levers, traditional contract management quickly shows its limits. Multiplication of versions, endless e-mail exchanges, delays in validation. All these factors slow down transactions and weaken relationships with customers and partners alike.
Reduce human error and legal risks
Manual management entails the risk of incorrect data entry, poorly integrated clauses or multiple versions circulating in parallel. With an automated system, templates are standardized and validated upstream by legal teams, limiting discrepancies and reinforcing compliance.
Save time and increase operational efficiency
Automation eliminates many repetitive steps: copying and pasting, printing, mailing or manual reminders. Signature times are reduced, and teams can concentrate on higher value-added tasks, such as negotiation or customer relationship management.
Improved collaboration between teams
A shared digital environment streamlines exchanges between departments. Sales, legal, purchasing and HR all work on a single, validated version, limiting the need to go back and forth, and speeding up decision-making.
Greater visibility over the contractual life cycle
A centralized tool enables precise tracking. You know where each contract stands, which clauses have been modified, which signatures are still awaited. This visibility gives managers greater control over progress and reduces bottlenecks.
What types of contracts can be automated?
Not all contracts have the same complexity or processing volume. Some require a high degree of personalization and legal follow-up, while others are based on recurring models that lend themselves perfectly to automation. Identifying these categories of contracts is a decisive step in knowing where to focus your efforts, and in rapidly achieving measurable gains:
- Sales and purchasing contracts: Commercial contracts, whether for product sales or supplier purchases, are particularly well-suited to automation. Standardization reduces time-to-completion and secures transactions.
- Employment contracts and HR: Human resources departments manage a large volume of contracts, including new hires, amendments and contractual terminations. The use of predefined templates speeds up creation and reduces errors.
- Service contracts: External service providers often require contracts covering duration, scope and remuneration. Automation facilitates their creation and monitoring, particularly in the event of renewal.
- Confidentiality agreements (NDA): Confidentiality agreements are short but very frequent, especially in the commercial negotiation phase. Automating the generation and signature of NDAs helps to streamline this stage without slowing down discussions.
Automation tool features
Implementing a contract management solution means more than just digitizing the signature. A truly useful tool must cover the entire contract lifecycle: creation, validation, monitoring and archiving. To achieve this, a number of functions are essential for greater speed, security and transparency.
- Pre-configured contract templates: The availability of templates validated by legal experts means you can quickly create compliant documents, without having to start from scratch every time.
- Electronic signature and authentication: The electronic signature secures commitments and speeds up the process. It is legally recognized and replaces handwritten signatures.
- Version tracking and audit log: every modification is recorded, avoiding confusion between different versions of the same contract and providing complete traceability.
- Automated notifications and reminders: The tools can send alerts about upcoming deadlines, such as a contract renewal or termination date. This avoids oversights and unexpected terminations.
- Integration with business tools (CRM, ERP, etc.): Connecting contract management to existing software (CRM, ERP, document management) ensures data consistency and reduces manual re-entries.
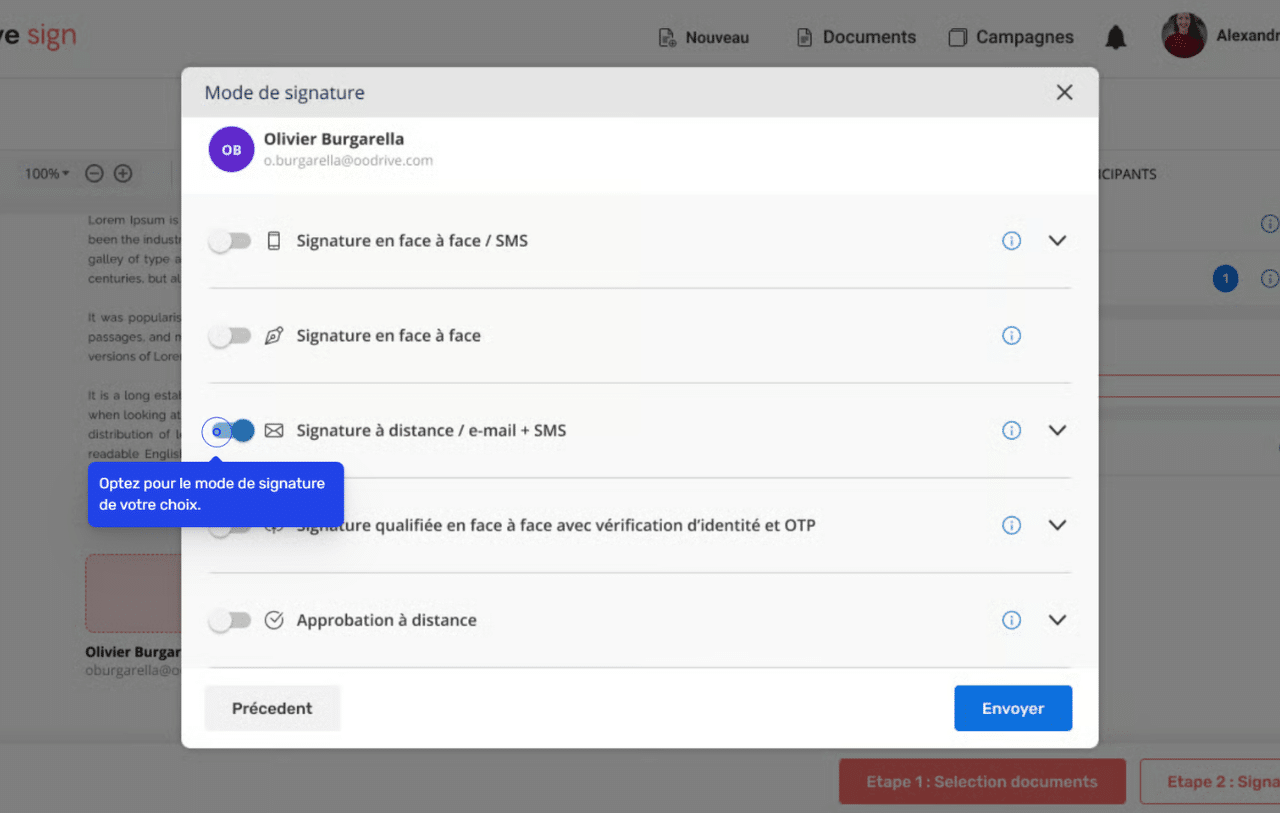
Concrete steps for implementing contract automation
Switching from manual management to an automated system doesn’t happen overnight. It’s a structured project that requires analysis of current practices, selection of the right technology and support for teams adopting new tools. By following a clear approach, you can secure the transition and rapidly reap the benefits of automation.
- Analysis of needs and existing processes: Before deploying a solution, we need to map current practices: types of contracts managed, volumes, average lead times, bottlenecks.
- Choosing the right technological solution: The market offers many specialized platforms. The choice should be based on the company’s objectives, budget and compatibility with existing tools.
- Creation of customized contract templates: Legal experts define standard templates that serve as a basis. These templates are then integrated into the tool and made accessible to all teams.
- Team training and change management: Training, documentation and support are needed to help users adopt the solution.
- Performance monitoring and continuous improvement: Once the solution is in place, regular analysis of processing times, volumes processed and team feedback is required to adjust processes.
How an API can simplify this process: the example of Oodrive
Integrating an electronic signature API into a contract management system makes the process even easier. With Oodrive’s solution, teams can send documents for signature without leaving their work environment.
This reduces lead times, minimizes errors associated with manual handling and enhances traceability. Every action is recorded and time-stamped, providing legal proof in the event of a dispute.
The API integrates with existing solutions (CRM, ERP, document management) and centralizes data in a single space. Information is updated in real time, and security is ensured by advanced encryption and strong authentication.
The impact of automation on legal and sales teams
Automating contract management frees lawyers from repetitive tasks (initial drafting, version tracking, reminders) so that they can concentrate on clause strategy and negotiation support, while sales teams shorten their signature times, free up time for customer relations and speed up the transition from quotation to contract. By working in a single, shared space (validated templates, approval workflows, audit logs), exchanges between legal, sales, purchasing and finance teams become much more fluid, with fewer back-and-forth e-mails, fewer misunderstandings about the “latest version”, and faster approvals, thus reducing administrative bottlenecks and better aligning everyone’s priorities.
Trends and developments to watch
Three dynamics are taking shape: generative AI, which produces draft contracts from simple instructions and accelerates the scoping phase; blockchain, used as an unforgeable register of signatures and versions to reinforce traceability and authenticity; and the move towards a fully digital contract cycle, from creation to archiving, where workflows, signatures and conservation are integrated, with human intervention refocused on negotiation and exception management.