Email deliverability refers to the ability of emails sent to reach their recipients’ inboxes without a hitch. According to the definition of the ISPs (Internet Service Providers, which refers more broadly to email address providers such as Gmail, Hotmail, Orange, etc.), deliverability only measures the percentage of emails sent that have reached their recipients, without differentiating between messages arriving as spam and those arriving inbox.
In this guide, we will use a different definition of email deliverability: the percentage of emails sent that reach the recipient’s main inbox, not counting those that arrive as spam. After all, isn’t that what good marketers are most interested in, how many prospects see their emails go through their inbox?
From the moment it is sent to the moment it is received, the journey of an email is comparable to an obstacle course. But what are the different factors influencing the difficulty of this event?
Sommaire
How does email deliverability work?
It is important at this stage to understand the stages that an email goes through when it is sent.
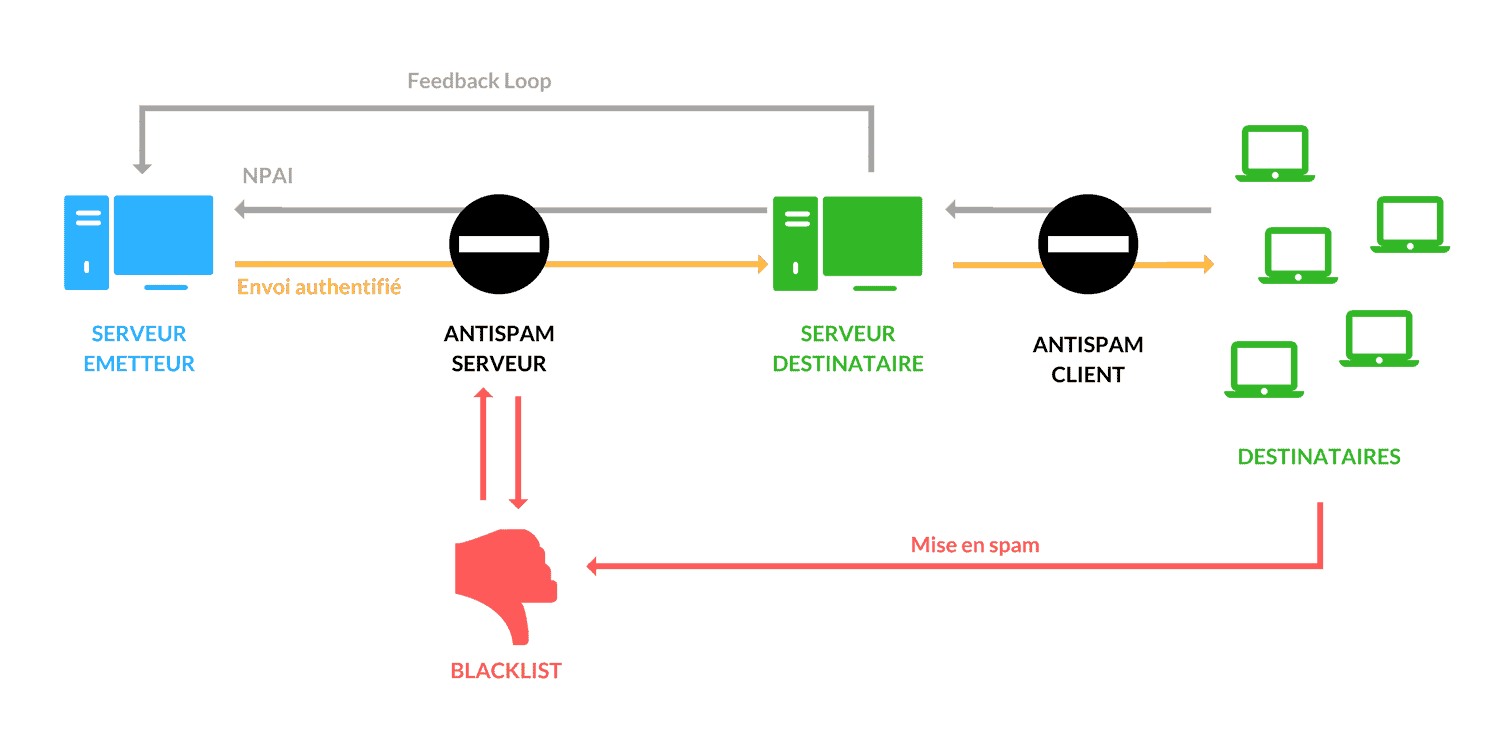
- When the sending server sends an email, it goes through the server’s anti-spam system, which checks that the message does not come from a blacklisted address or that previous mailings have been successful.
- Once the email arrives at the destination server, the server may issue a NPAI (No Longer At Home Address – also known as a “bounce”) message to indicate that the address does not exist, and therefore the email cannot be delivered.
- If the e-mail has correctly passed these first stages, it is then transmitted by the server to the recipients. During this transmission, it passes through the client antispam which will analyse the content of the message (HTML code, text, images)
- If it is not considered spam, and the recipient does not bounce (e.g. if the box is full), the mail will finally arrive in the recipient’s inbox.
- In the event that a reader considers, after reading the e-mail, that it should have been classified as spam, he or she can carry out the spamming himself or herself. This action will then have a direct consequence on the blacklist of the ISP concerned.
- In order to monitor and deal with the various complaints related to his mails, the sender can have access to the feedback loop of the different ISPs. This will allow the sender to analyse which type of readers are complaining about his emails, and thus remove them from his lists in anticipation of his next mailings.
So we’ve gone through the whole obstacle course that your emails have to jump through to reach their destination.
In the rest of this guide, we’ll look at the various aspects of deliverability, how ISPs distinguish between good and bad performers, and what all marketers can do to ensure their campaigns reach the recipients’ inboxes.
Do you have delivery problems?
If you are reading this guide, you probably have problems with the deliverability of your emails. So, before talking to you about all the best practices to follow, we are going to present you with the solutions that you can apply in the short and medium term to improve deliverability.
Short-term steps
Case 1: You are blacklisted by an ISP
If only some of your emails are not delivered, it is very likely that some ISPs will blacklist you.
This means that they will systematically block your domain or sending address, and your recipients will no longer receive your emails.
- Check your email deliverability rate by ISP and compare it to your average deliverability rate to detect blacklisting.
- If this is the case, clean up your email database ( DataValidation is recommended for this) and contact individual ISPs to resolve the situation.
Case 2: You are blocked by your router
If none of your emails have been delivered, it means that you have been blocked by your router due to a high bounce rate, for example.
If this is the case, you will also have to show your router a clean bill of health and provide guarantees that your deliverability will be improved so that it agrees to lift your block. Indeed, the router has no interest in tarnishing its reputation by letting many SPAM messages be sent through it.
- Tighten your customer segmentation on people who have opened your emails in the last 30 days, study the open rate by ISP and remove from your list contacts who have not been opened for over 18 months.
Medium-term approaches
Analyse your indicators by ISP
A common misconception is that the email deliverability rate is the same as the ISP accepting your email.
This is not the case. It is quite possible to have a 90% acceptance rate but a 10% open rate, as all the rest of your mail will be SPAM.
You should therefore consider email deliverability as the fact that it reaches its recipient, and not as SPAM.
- Consider looking at the open rate per ISP and compare it to the average open rate to detect possible delivery problems.
Work structurally and iteratively on segmentation
We don’t remind you often enough, but the segmentation of your mailing lists is an essential element if you want to solve deliverability problems in the long term.
It is important to adapt the frequency and content to each customer group and their needs.
You will then send fewer emails to those who cannot handle too much pressure, and they will not report you as SPAM.
- Regularly test segmentation by playing on different attributes of your customer lists.
Best practices in email deliverability
Do you want to go further than just solving deliverability problems? Let’s take a look at the best practices to ensure that your emails arrive safely.
The technical settings required for good email deliverability
1. Choose between shared or dedicated IP address
Email services keep a close eye on the reputation of IP addresses. To optimise your email deliverability, it is essential to ensure that your address maintains a good reputation. In email marketing, two types of IP addresses can be used:
Shared IP address
An IP address used by several senders.
- Advantage: More affordable price
- Disadvantage: Your reputation depends on the practices of other senders
Dedicated IP address
An IP address used by a single sender.
- Advantage: You are the sole master of your reputation
- Disadvantage: Higher price with no guarantee of better performance than a reputable shared IP
It is therefore understandable that the choice between shared or dedicated IP addresses depends very much on their reputation. If you are on a shared IP address, changing to a more expensive dedicated IP address only makes sense if your current reputation is bad. To find out what your current reputation is and decide whether or not you need to change, we recommend this article on how to find out your sender reputation.
2. SPF, DKIM and DMARC protocols
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
This protocol makes it possible to check that the server used for sending corresponds to the domain name indicated, which thus limits identity theft. To respect this protocol, you must publish a TXT record on the DNS server of your domain name. This record will indicate the list of IP addresses authorised to send mail with your domain name.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
This protocol consists of associating a domain name with a message by integrating a digital signature in the message header. DKIM thus makes it possible to check both that the domain name has not been usurped and that the message has not been altered during transmission. To set up a DKIM signature, you must :
- Create a private key/public key pair in 1024-bit RSA format
- Publish in your domain’s DNS the public key
- Configure the sending of your messages for encryption with the private key
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance)
This protocol is a complement to SPIF and DKIM. It allows reports to be generated on the tests carried out from SPF and DKIM, and thus to receive the results of the authentication of the mailings. The recipient’s mailbox can also find out how it should handle mail that has not passed the identification test.
To learn more about these topics and to be able to use these protocols, you can read this article on the benefits of SPF, DKIM and DMARC.
Deliverability is a marketing job
As you can see, the reputation of your IP has an important influence on your deliverability. But it also depends on the reputation of your domain and your senderscore. To group these three notions together, we talk about sender reputation.
This sender reputation is directly linked to the engagement of your readers with your messages. The open rate, click rate and response rate are all parameters that need to be improved in order to achieve your ultimate goal: generating engagement.
1. Target correctly
In email marketing, knowing your target audience is vital. This can help you to address only those people who really correspond to your content or your offer, but also to adapt your messages.
Good targeting means ensuring that all the contacts on your list are potentially interested in what you have to offer, and therefore more likely to open, read or respond to your message.
But knowing your target audience can also help you assign an appropriate pressure (sending frequency). If the pressure is too strong for your reader, they will not read all the emails they receive from you, and therefore their commitment will automatically suffer.
Finally, it is also important to remove bounces and regularly clean up your email lists with a tool like UseBouncer.
2. Work on your object
The subject line of an email is the first window of your message (and more broadly of your company) to your prospects. It is therefore the main reason why the message will be opened or not. Optimising it therefore directly influences the opening rate of your emails.
There are a number of good practices to follow: don’t leave the subject line blank, avoid capitalized words and the abuse of exclamation marks and question marks, and don’t use vocabulary directly related to sales. The subject line should make it clear that you are trying to provide value to the person you are talking to.
To further arouse the recipient’s curiosity, inserting personalization elements in the subject line can considerably increase the open rate. Who wouldn’t be tempted to open an email mentioning the name of their company, for example?
3. Take care of your content
Producing content that is valuable to the reader, well formatted and pleasant to read, ensures their enjoyment and therefore their level of interaction with your message (click or reply).
However, keep an eye on the ratio of your content between text and HTML code: a poor ratio could penalise the email when it passes through the anti-spam system. Also avoid inserting large or too many images and attachments.
As with the subject line, this content can also be enriched by customising it for the recipient. Inserting the contact’s name or other information in your message will arouse their curiosity and encourage them to read it more carefully.
Finally, don’t forget to give the reader the option of unsubscribing from your contact list in your message.
To learn more about the best marketing practices to take care of your deliverability, we recommend you read this article on 29 ways to avoid spam.
The best tools for email deliverability
To complete this guide to email deliverability and the four steps to solving problems, we have chosen a selection of tools to optimise your emails and your deliverability rate.
We will introduce you to tools for :
Monitor your email deliverability
Poor deliverability doesn’t have to be the case: there are tools to check your configuration and reputation before sending your campaigns.
[Tool] ScanMy.Email
- A complete (and free) checklist to validate your configurations. This is designed by Simon Bressier, the head of deliverability at Sendinblue (the French leader inemail marketing)
[Tool] SendForensics
- Test the deliverability of your emails
- Compare your deliverability to the average in your sector
[Tool] Content Spam Checker
- Scans your emails for words categorized as SPAM by anti-virus software
- Increases email deliverability by over 30%.
[Tool] 250ok
- Tool palette scanning your configuration
- Scans the reputation of your domain
Clean up your customer database
Another important parameter to take into account and often unknown to the general public is the existence of all the email addresses of the recipients of your emails.
Indeed, sending emails to non-existent recipients will often cost you money and lower your deliverability rate.
Worse, it can damage the reputation of your shipping domain name. It is therefore essential to test the existence of email addresses in your contact list.
[Tool] Octolis
- Allows you to check phone numbers and email addresses in bulk
- Import your contact file or connect your CRM
Tools to optimise the content and code of your emails
While it may not be obvious at first, the HTML code behind each of your emails has a direct influence on your deliverability rate and is not always the same as that used for a web page.
La redondance ou l’utilisation de codes non supportés par certains clients emails sont des écueils courants à éviter à tout prix.
<!–
[Tool] CSS Inliner
- By Campaign Monitor
- Paste your HTML code, get your styles online
- Allows you to inject optimised style for email
->
[Tool] PreMailer
- Copy your HTML or enter a URL
- Compresses and optimises code for email
- Add parameters to URLs en masse
[Tool] CSS Inliner
- By MailChimp
- Paste your HTML code, get your styles online
- Allows you to inject optimised style for email






