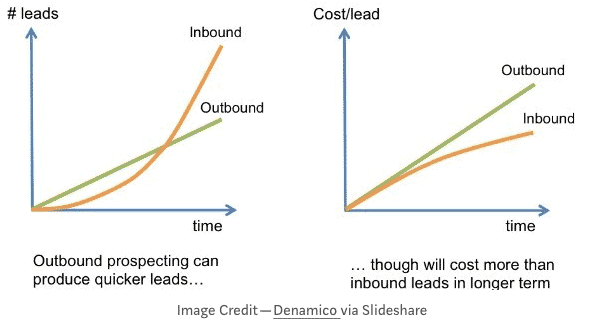
Implementing a B2B outbound strategy is not easy when you are starting a business. The inbound strategy, i.e. “inbound prospecting”, generally allows after a few years to generate 5 times more leads and 5 times more conversions than an outbound approach. However, inbound is not always suitable for all companies and at all times, because it takes time for this strategy to produce results. It is not a matter of days or weeks, but months or years. This is where outbound is particularly effective in converting sales quickly at the start of a business.
Depending on the maturity of your business and your financing capabilities, executives and sales managers need to make the right choice between an inbound, outbound or hybrid sales strategy. Companies usually decide to adopt a hybrid sales strategy. Until your inbound strategy starts to bear fruit, outbound becomes more than essential.
Outbound sales are faster and have a relatively short turnaround time with faster results. When an outbound strategy is done on a large scale and executed well, it can generate more revenue than inbound.
In this article, I’m going to talk about getting to grips with outbound sales and what to put in place at the start to increase your effectiveness.
Sommaire
How do you plan your outbound business development?
Implementing an outbound strategy is a great idea, but it depends a lot on the effectiveness and productivity of your sales teams. To get them off to a good start, you can set a direction and then gradually adjust the process according to your needs and observations.
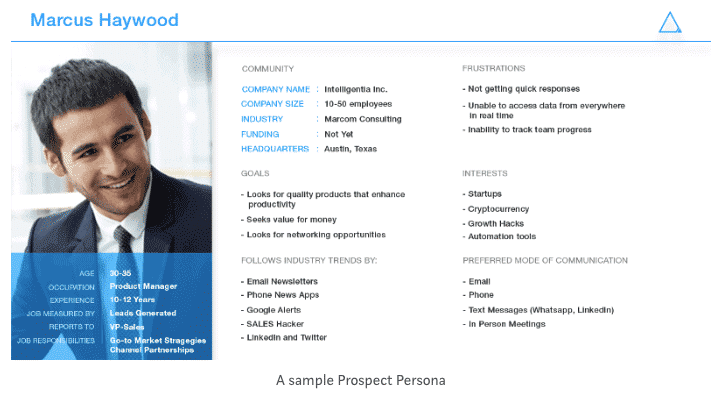
1. Get off to a good start: define the profile of a typical prospect
A building can withstand storms when the foundation is solid. Step 1 of any inbound or outbound strategy is to identify your typical prospect (or persona) in advance. You need to know who you are targeting and why.
The sooner you get this, the sooner you can pick up your pace. This means taking the time to determine the personality of prospects from a sales perspective (the widely used buyer persona is very useful to marketing and delves into a lot of useless information that salespeople don’t need to waste time looking for).
2. Define your company’s first sales process
As a founder, you should make the first ten sales yourself. By doing so, you will get a good idea of how your ecosystem works. Formulate your journey even if it is only six steps on paper. This will give the sales manager or new salespeople a practical basis and framework to work on and refine over time.
Don’t expect everything to be perfect, because as technology evolves, sales processes will quickly become obsolete. For example, ten years ago, social selling was of negligible importance, whereas today it produces prodigious results.
3. Set realistic sales targets for your sales team
Once you have made the first ten sales of your business yourself, you will have a clearer idea of what is achievable.
Depending on the length of your sales cycle and the stakes involved, 200 customers per month can be just as credible as 2 per year.
Pro tip: most sales require at least 5-10 points of contact before a sale is made, so be very clear about your expectations.
4. Equip and train them well
Outbound sales are all about numbers. The more you optimise your time and methods, the more sales you will convert.
Well-equipped and well-trained sales teams will be able to reach more people, organise more demonstrations and meetings and thus generate more revenue.
The tools you need:
- A lead generation tool to extract email and personal information from prospects. You can use tools such as Hunter.io ($39/month for searching 1,000 leads), Alore’schrome extension to find emails, Dux Soup ($15/month), etc.
- A solid CRM to take care of your data. You can try Alore CRM, (Free for up to the first 100 leads and $49/seat/month for over 1000 leads) Pipedrive, ($29/seat/month for a normal package) Zoho CRM or Salesflare ($35/seat/month)
- A tool for youremailing campaigns to plan the sendings and follow the results. You can use tools such as Mailshake ($29/person/month for the basic package) Pic ($40/seat/month for the basic package), Alore CRM (free for the first 100 leads and $49/seat/month for 1,000 leads or more)
- A “Click to call” tool to make, record and report outbound calls. You can use tools such as Hubspot calls, Alore CRM (Free for the first 100 leads and 49 USD / seat / month for more than 1,000 leads).
Training :
- Create call scripts and sample letters as a starting point for your sales teams.
- Teach them how to respond to objections and get appointments.
- Train your teams on your product or service accurately. This type of training should be done on a regular basis to ensure that every new feature or change is clear to every member of the team.
- Sales success is the result of both teamwork and individual performance. Make sure you instil the company culture and team spirit from the start. A team is always more productive than the sum of its parts.
5. Sales aids
A sales team may be talented and motivated but they will still need external help to perform. This takes the form of the tools and training mentioned above, but also of effective marketing support. This can include buying prospecting lists when you are starting from scratch (although it is better to focus on buying your own lists, enriching them with additional data, as they convert much better than the one you buy).
6. Motivating your teams
Depending on the nature of your business, you need to create bonus and commission programmes. Here are some ways to create your program to incentivize your teams.
a) Assigning targets at several levels
Having three levels in your goals will keep most salespeople motivated to reach the first level even after a bad month, and exceed the highest level in most cases.
b) Gamifying sales
Creating an internal competition for your sales teams and awarding a prize to the best performer is seen as an extra incentive.
Tip: Try to keep the prize non-monetary. This helps to infuse a healthier competitive spirit.
c) The bonus programme
Implement a quarterly bonus. This works better than an annual bonus to keep teams motivated. Of course, if you have the budget, keep both!
d) Maintaining a public ranking
Keeping a public ranking often helps to motivate the team members who are struggling the most and gives them more motivation to achieve their goals so that they are not at the bottom of the ranking.
Tip: Outbound salespeople should receive 2 to 3 times more commission than inbound salespeople.
7. The right person for the right job
Salespeople with a lot of experience tend to perform better on inbound sales and convert faster. They know the right thing to say at the right time, handle objections better, etc.
Less experienced salespeople, when well trained, are excellent with outbound leads, mainly because of the need for quantity and their much higher energy level.
8. Create a backup – Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
It is dangerous to rely on a handful of salespeople to drive your sales performance.
What if they decide to leave and you can’t do anything to keep them? They will leave with all their contacts.
The best salespeople are reluctant to share all the tips they know with their colleagues, so find a way to make them contribute to the collective success in a positive way.
Set up mentor-sponsor programmes. If your team is large enough, ask the more experienced salespeople to mentor the newcomers, and give them bonuses based on the performance of the one they supervise.
Set up incentives or a game to motivate your sales people to keep the CRM up to date and to ensure that progress is shared with their managers.
Deployment of your Outbound strategy
Now you have your target well defined, a process in place and the sales team is motivated and excited to get started. Now it’s time to find prospects.
Once you have a good understanding of your typical prospect, you will be able to find out what their preferred means of communication are: email, telephone, social media, live events, forums, etc.
Step 1: Brainstorm with your sales team
You should check with your sales team what criteria they use to determine their priority list.
Are they prospecting 100 companies at once or are they segmenting them into batches of 20 and prioritising them?
Let’s assume that design agency owners are your target market. Here’s how to segment the data:
- Step 1: Make a list of agency owners by location: UK, USA, Canada, China, Singapore, etc.
- Step 2: Next, segment the data according to company size, funding status, etc.
- Step 3: Enrich these short lists using tools such as Full Contact or ClearBit on all publicly available information about the person and the company.
Next, you need to prioritise the segments according to key criteria:
- In how many cities are they present (indicates their growth and dependence on existing automation and communication processes)
- Do they attend a lot of events lately (shows activity and willingness to act, and that engaging them at events might be a good plan)
- Is the management active on social networks (indicates an open culture and easier access)
- Number of marketers in the team (LinkedIn makes this clear)
- Sponsorship
- Collaborations etc.
Based on indicators such as these, you will be able to create sets of people to whom you need to speak.
Now that your target list is ready, it is time to go into execution mode.
Cold emails
Cold email campaigns can produce very good results when done correctly.
Personalisation and relevance are the key to conversion. The more you personalise your email campaign and get a good conversion rate, the more you will sell.
Here are some quick tips:
- E-mail delivery rates depend on the reputation of the sender: make sure you use a reliable e-mail service provider to plan your e-mail campaigns.
- Email open rates depend on the timing of the email and the relevance of the subject line. Think carefully about the subject line and the timing of the email according to the recipient’s local time zone.
- The response rate / click-through rate depends on the personalisation of the email and an effective call-to-action (CTA).
Cold calls
Cold calling is not dead. In fact, they are a great way to find new customers for many sectors.
However, modern customers are more careful with their time and choices. It is imperative that sales people put all the chances on their side by having researched the person thoroughly and avoiding the feeling that their potential customer is just another name on a prospecting list.
As a founder, it is advisable to listen to your salespeople’s first calls to see what is not working in the script. This will allow you to determine what types of pitches prospects are most sensitive to.
Here are 3 techniques that work best to hit your prospect:
- Bounce back on company news (fundraising, new products, etc.)
- Know the exact role of the person and make sure you understand the expectations of that role. This is essential to building a relationship with your prospect. This should be your priority.
- Have a common interest that is not work-related (easy to spot on Facebook or Twitter). For example, an interest in travel, basketball, etc.
Cold call 2.0
This is the modern version of cold calling popularised by Aaron Ross of Predictable Revenue.
Aaron’s strategy is very neat and worked wonders back when he developed this at Salesforce. Here’s how it works:
Let’s say you want to call Samantha in Salesforce:
- Step 1: First call Jim in marketing and ask him very subtly to put you in touch with the right person in sales.
- Step 2: Most likely, Jim would put you in touch with Samantha or her colleague.
- Step 3: Now, when you call Samantha, you say that Jim has referred you to her and that you would like ten minutes of her time.
So it’s not really a cold call anymore and Samantha will listen to you more carefully as her colleague has passed the call on to her. You have thus lowered her guard against random phone calls and you have a point.
This method can easily be transferred to cold emails.
Social selling
Social selling is a major component of modern outbound sales. It is a great way to interact with prospects on social networks by commenting on posts, liking, etc. and then gradually trying to build a relationship with them by phone or email.
However, this method does not produce immediate results and takes time.
Professional events
This is an outbound strategy that may be appropriate but is expensive and uncertain. Expensive, of course, because you have to pay to set up stands or send participants to these events.
Uncertain, because unless you are the one organising the event, you can only rely on other companies and organisations to organise it. However, sales people who attend and make good contacts with participants can generate quality leads.
Attending events is a good experience because it helps you to understand your prospects and the competition. However, don’t have the same people attending all the time so that all your sales people can benefit from the experience.
In conclusion:
Outbound sales are a great way to build momentum once you have identified your typical customer profile.
As a founder, it is important that you handle the first 10 sales yourself. This will give you a good understanding of the reality of your market.
Thereafter, the founder must spend time putting in place internal processes, tools and methods to keep their sales teams on track and motivated through appropriate training, incentive programmes and external support.
Then decide on a strategy and implement it with conviction.






